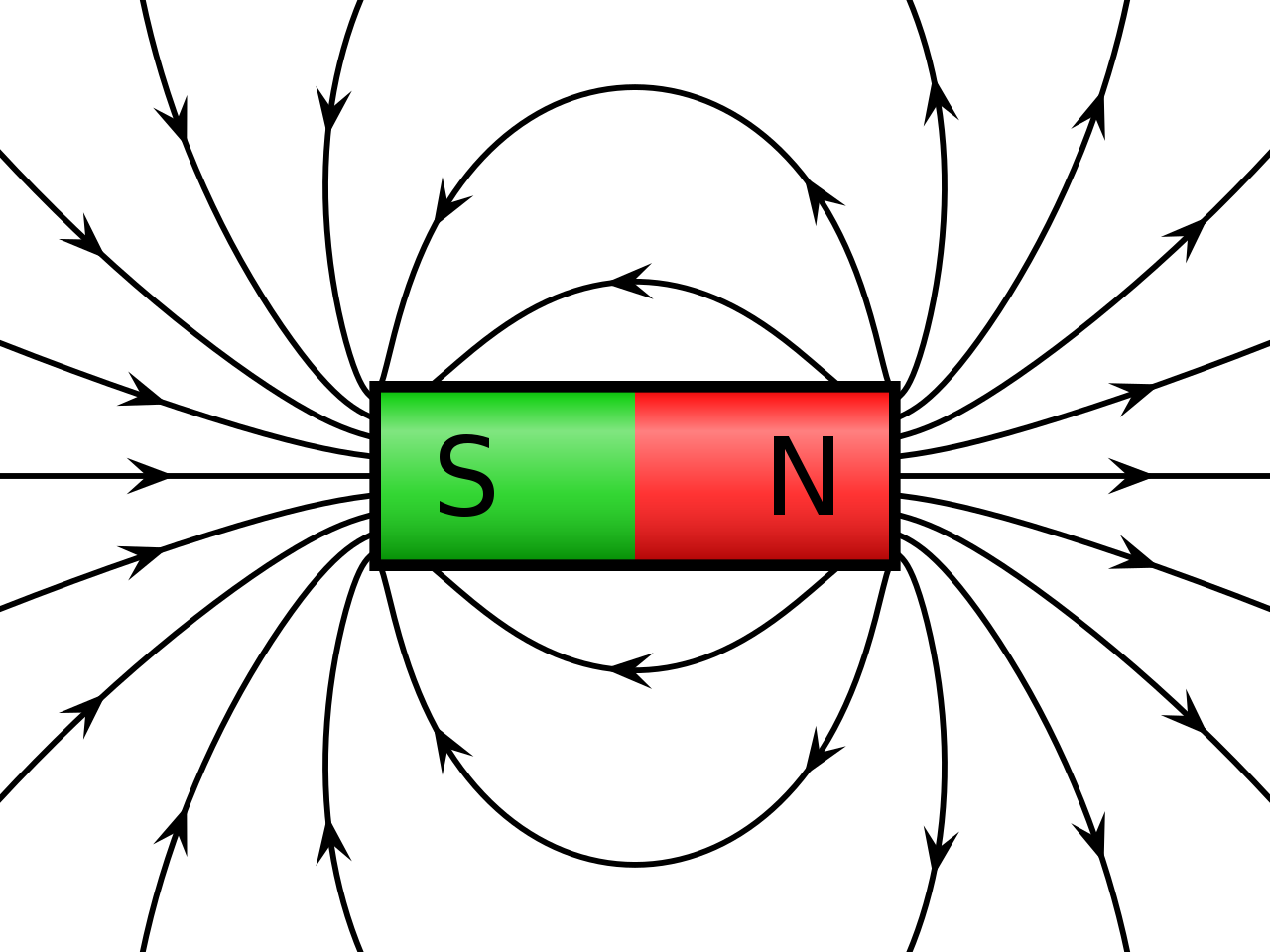
 Permanent Magnet
Permanent Magnet
Permanent magnets are materials where the magnetic field is generated by the internal structure of the material itself. Inside atoms and crystals you have both electrons and the nucleus of the atom. Both the nucleus and the electrons themselves act like little magnets, like little spinning chunks of electric charge, and they have magnetic fields inherent in the particles themselves. There's also a magnetic field that's generated by the orbits of the electrons as they move about the nucleus. So the magnetic fields of permanent magnets are the sums of the nuclear spins, the electron spins and the orbits of the electrons themselves. In many materials, the magnetic fields are pointing in all sorts of random directions and cancel each other out and there's no permanent magnetism. But in certain materials, called ferromagnets, all the spins and the orbits of the electrons will line up, causing the materials to become magnetic. This would be your normal iron, cobalt, nickel. Permanent magnets are limited by the structure of the material. And the strongest magnetic field of a permanent magnet is about 8,000 gauss. The strongest magnets here at the Magnet Lab are 450,000 gauss, which would be almost 50 times stronger than that.
Who supplies high quality Strong Neodymium (NdFeB) Magnet - Rare Earth Magnets?
Magnosphere offers best priced Neodymium magnets globally to all industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Military, Advertising, Design House, Electronic and Academic/R&D. Please inquire for custom Neodymium magnets or magnetic assembly.
Strong Magnets (Rare Earth Magnets) and Magnet Material
Magnosphere stocks alnico magnets, bonded magnets, ceramic (ferrite) magnets, flexible rubber magnets, neodymium iron boron (NdFeb) magnets and samarium cobalt magnets along with magnetic material assemblies for fabrication and distribution. Many standard magnetic alloy materials, grades, and geometries (shapes) are available for immediate use. Magnosphere will also fabricate from inventoried permanent magnet materials to your specific requirements.
Diversity exists between the varieties of magnetic alloy materials and grades. Each permanent magnetic material has unique advantages and disadvantages. We suggest that you contact our customer support team so your application can be reviewed. We will then be able to select appropriate magnetic material for your application.
A brief description of commercially available magnetic materials is listed below. A more rigorous explanation and technical characteristics of the various magnetic alloy materials are available on their individual pages.
Magnetic Alloys
Below is a list of the magnetic materials we have available for assemblies:
Alnico Magnets
Alnico magnets are used primarily in technical applications, where temperature stability is critical.
Characteristics: Excellent for high temperature applications up to 1,000°F, high residual induction, and corrosion resistant. Cast alnico magnets can also be produced in relatively complex shapes.
Sizes and Shapes: Discs, Rods, bars, and horseshoes.
Applications: Commonly used in Meters, and for specialized holding, high-temperature applications.
Alnico magnet alloy is largely comprised of Aluminum, Iron, Cobalt and Nickel. Alnico is a moderately expensive magnet material because of the Cobalt and Nickel content. Alnico magnet alloy has high maximum operating temperature and very good corrosion resistance. Magnets made with this alloy are available in a variety of grades and dimensions and are usually cast and finish ground to size. Alnico magnet material is an older technology and it has a rather low Energy Product (BHmax). Alnico magnet alloy is now mainly used in military, aerospace, older proprietary designs and in applications where the magnet will be exposed to elevated temperatures.
Rare Earth Magnets
Samarium Cobalt Magnets (SmCo) and Neodymium Iron Boron Magnets (NdFeB) are called Rare Earth Magnets because Neodymium and Samarium are found in the rare earth elements on the periodic table. Both Samarium Cobalt and Neodymium magnet alloys are powdered metals which are compacted in the presence of a strong magnetic field and are then sintered.
Neodymium Magnets (Rare Earth)
(NdFeB) Neodymium, a rare earth magnet, is made up of Neodymium Iron and Boron and is moderate in price. With poor corrosion resistance, a neodymium iron boron magnet is usually plated or coated (Examples: Nickel Plated, Epoxy Coated, Parylene Coated). Neodymium magnets are offered in a range of operating temperatures depending on your application (80°C to 200°C). Premium Neodymium magnetic materials capable of operating above 120°C can become quite expensive. This permanent super magnetic material has many intellectual property rights associated with it and there are a limited number of licensed manufacturers in the world. Many infringing manufacturers from the Pacific-rim dump subpar magnetic material into the Western markets. This magnetic material is extremely powerful and it has allowed for the downsizing of many products from HDD (Hard Disc Drives) and motors to novelties and audio devices. Neodymium permanent magnets usually offer the best value when comparing price and performance.
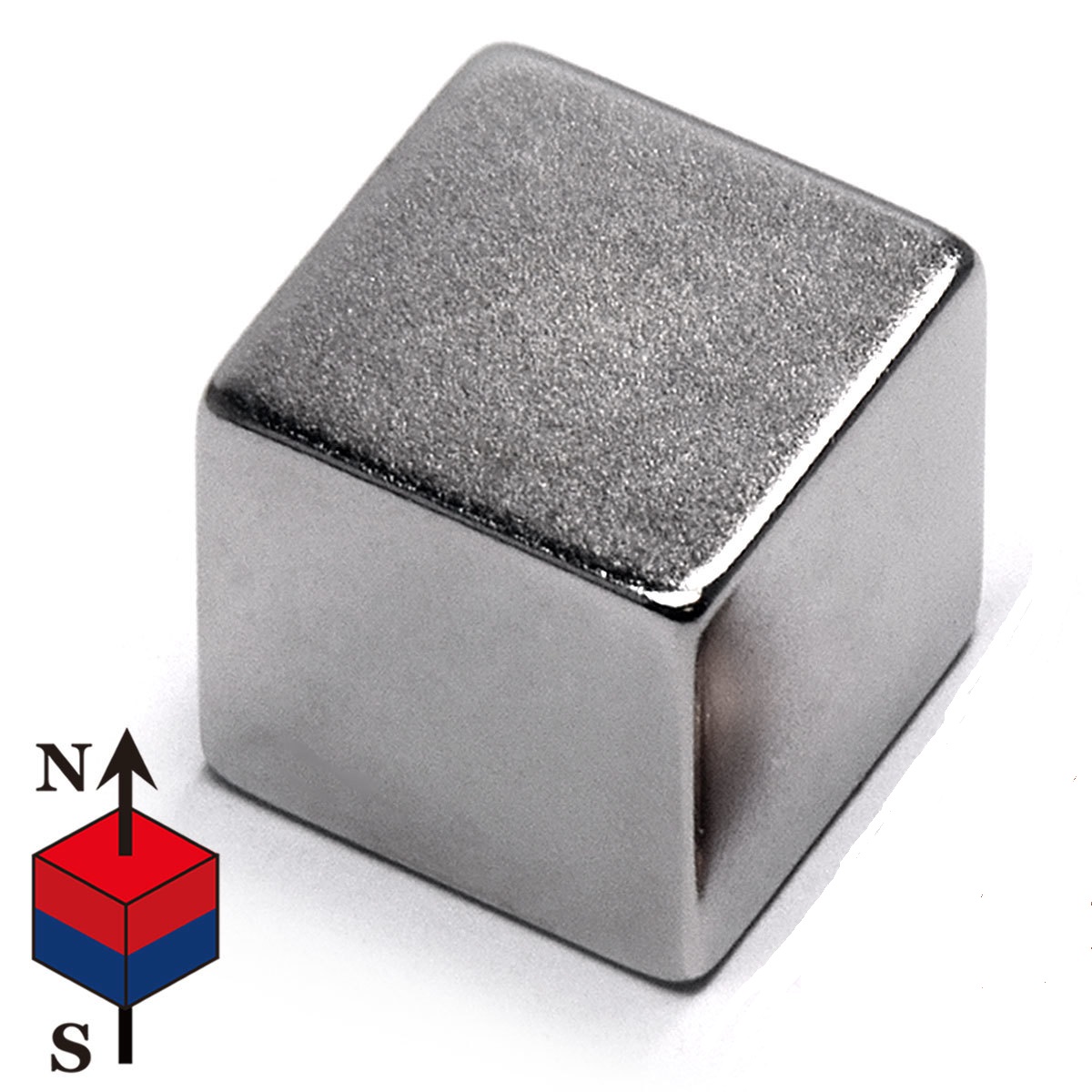
- What is a neodymium magnet? Neodymium magnets are strong permanent magnets, and part of the rare-earth magnet family. They are also referred to NdFeB magnets or NIB, as they are composed mainly of Neodymium (ND), Iron (Fe) and Boron (B).
- Why are neodymium magnets so strong? Neodymium magnets are considered strong because they resist demagnetization and have a high saturation magnetization. Although neodymium magnets are more costly than ceramic magnets, these super strong magnets pack a powerful punch! With neodymium magnets, you can use a smaller sized magnet to achieve the same objective. This can potentially lead to a lower overall cost, as the size of the entire device can shrink.
- How long do neodymium magnets last? Neodymium magnets will likely lose less than approximately 1% of their flux density over a 100-year period if their physical properties remain intact.
- What are the main characteristics of neodymium magnets? Neodymium magnets are far less subject to cracking & chipping and less costly than other rare-earth magnetic material such as Samarium Cobalt ("SmCo"). They are however, more sensitive to temperature. For applications where this is critical, SmCo may be the better choice, since its magnetic properties are very stable at elevated temperatures.
- What grades & shapes are available for neodymium magnets? Grades 30-52 of Neodymium magnets are available in disc, rectangle, square and rod shapes, and can be custom manufactured to meet your specialty requirements.
- What are some common applications for neodymium magnets? Neodymium Magnets are typically used in audio equipment (microphones, headphones, and loudspeakers) hard disk drives, pumps, bearings, MRI scanners, electric vehicles, wind generators, high performance motors, actuators, magnetic therapy, anti-lock braking systems, levitation devices, door latches, model making, arts & crafts, home improvement (DIY-fixing furniture, hanging pictures etc.) POP displays & more.
- What are the best temperatures to use for neodymium magnets? Neodymium magnets should not be used in temperatures above 130° C(240° F) without careful magnetic circuit design. Please contact us to discuss your application with our engineers if you plan on using these magnets above this temperature.
- Do neodymium magnets require surface treatments? Neodymium magnets that are not protected with a surface coating (such as plating) may rust in humid conditions. (top)
- What common bonding applications are used for neodymium magnets? Neodymium magnets are often assembled into products using “super glues” such as Loctite 325. As with all bonding applications, please ensure that bonding surfaces are clean and dry (prior to bonding) for best results.
- What is a permanent magnet? Permanent magnets represent the majority of magnetic materials available today. A permanent magnet is made from ferromagnetic materials, which have magnetic fields that do not turn on and off like electromagnets. We carry a large inventory of permanent magnets; neodymium, alnico, ceramic (ferrite) and samarium cobalt, in a wide variety of shapes, sizes and grades.
- What is a rare-earth magnet? Rare-earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets available today, and produce significantly stronger magnetic fields than ceramic (ferrite) or alnico magnets. There are two types of rare-earth magnets; neodymium and samarium cobalt, both of which are available for on-line purchase. Click here to learn more information about magnetic materials.
- How are magnets rated? Magnets are typically rated by their residual induction, coercive force & maximum energy product. This refers to the maximum strength that the magnetic material can be magnetized to.
- What does "approximate pull Info" mean? The approximate pull info listed for Neodymium magnets are for reference only. These values are calculated under the assumption that the magnet will be attached to a flat, ground 1/2" thick mild steel plate. coatings, rust, rough surfaces, and certain environmental conditions can significantly reduce the pull force. Please be sure to test the actual pull in your actual application. For critical applications, it is suggested that the pull be de-rated by a factor of 2 or more, depending on the severity of a potential failure.
- What safety precautions should be taken into consideration when working with neodymium magnets? Neodymium magnets are hard, fairly brittle, and high in magnetic strength. They can snap together with great force, so please ensure that all personnel handling these magnets are aware to handle them carefully in order to avoid injuries. They can also chip or break if dropped or if snapped together, so please take special care when handling these powerful magnets!
Samarium Cobalt Magnets (Rare Earth)
Samarium Cobalt, another rare earth magnet, is made up largely Cobalt and Samarium and is the most expensive magnetic material to manufacture and to fabricate. Most of the cost is due to the high Cobalt content and the brittle nature of the Samarium alloy. This permanent magnetic material offers high resistance to corrosion and can withstand high operating temperatures, up to 350°C. Samarium Cobalt magnetic materials are used extensively in the aerospace market or in areas of industry where performance is the priority concern and cost is secondary. Samarium Cobalt is the second most powerful magnetic material and exhibits excellent resistance to demagnetization.
- What are the main characteristics of samarium cobalt magnets? Samarium Cobalt Magnets exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, and do not need to be protected for corrosion. SmCo magnets also offer high-resistance to demagnetization. They are commonly used in motors, machinery, pumps, medical devices, magnetic couplings, magnetic separators and more.
- What are the best temperatures to use for samarium cobalt magnets? SmCo magnets are very temperature stable - their properties stay within a very narrow range up to about 300° C (570° F).
- What are some common applications used for samarium cobalt magnets? SmCo’s magnetic characteristics are ideal in applications for the marine, automotive, aerospace, medical, military and industrial automation industries where high- temperature performance is critical.
- What grades & shapes are available for SmCo magnets? SmCo magnets are available in a number of different grades that span a wide range of properties and application requirements. We currently stock SmCo disc magnets in grades 18 and 26, available in a wide range of sizes.
- What are recommended bonding applications for SmCo magnets? SmCo magnets are often assembled into products using "superglues" such as Loctite 325. It's best to avoid placing mechanical stress on this material, and always ensure that bonding surfaces are clean and dry prior to bonding.
- What are some safety precautions that should be taken into consideration when working with samarium cobalt magnets? SmCo magnets are hard, very brittle, and high in magnetic strength. They can snap together with great force, so please ensure that all personnel handling these magnets are aware to handle them carefully to avoid injuries. They can also chip or break if dropped or snapped together, so please take special care when handling these powerful magnets!
- What is a permanent magnet? Permanent magnets represent the majority of magnetic materials available today. A permanent magnet is made from ferromagnetic materials, which have magnetic fields that do not turn on and off like electromagnets. We carry a large inventory of permanent magnets; neodymium, alnico, ceramic (ferrite) and samarium cobalt, in a wide range of shapes, sizes and grades.
- What is a rare-earth magnet?Rare-earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets available today. Rare earth magnets product significantly stronger magnetic fields than ceramic (ferrite) or alnico magnets. The two types of rare-earth magnets are neodymium and samarium cobalt magnets, both of which are available for on-line purchase.
- How are magnets rated? Magnets are typically rated by their residual induction, coercive force & maximum energy product. This refers to the maximum strength that the magnetic material can be magnetized to.
Ceramic Magnets (Ferrite)
Ceramic magnet material (Ferrite) is Strontium Ferrite. Ceramic magnets are one of the most cost-effective magnetic materials manufactured. The low cost is due to the cheap, abundant, and non-strategic raw materials used in manufacturing this alloy. Permanent Ceramic magnets lend themselves to large production runs. Ceramic magnet material (Ferrite) has a fair to good resistance to corrosion and can operate in moderate heat. The majority of the worlds Ceramic magnetic material comes from China because of the alloys commodity nature and the high tooling costs found in the west. Ceramic (Ferrite) magnets have a low Energy Product and are usually used in an assembly containing mild steel.
- What are the main characteristics for ceramic magnets? Ceramic magnets are medium in magnetic strength, and can be used at fairly high temperatures. They are low cost, making them ideal for applications such as automotive sensors, magnetic separators, craft projects, badge holders, latches, display boards, science projects, toys, games & more.
- What grades & shapes are available for ceramic magnets? Grades 5 (most commonly used) through 8 are available in disc, block (rectangle & square) and ring shapes, and can be custom manufactured to meet your specialty requirements.
- What are the temperature constraints for ceramic magnets? Ceramic magnets can be used at fairly high temperatures, although their magnetic properties drop with temperature. At 175°C (350° F), approximately 75% of their room temperature magnetic properties are retained.
- How are magnets rated? Magnets are typically rated by their residual induction, coercive force & maximum energy product. Click here for more details (section 4.0). This refers to the maximum strength that the magnetic material can be magnetized to.
- What are some common applications for ceramic magnets? Common applications for ceramic magnets include raft projects, refrigerator magnets, badge holders, latches, display boards, loudspeakers, security systems, motors, generators & alternators, lifting magnets, eddy current devices, brakes, clamps, switches & relays, sweeper magnets, science projects, toys, games, motors, magnetic couplings, POP displays, advertising giveaways, promotional items, novelties & more.
- Are there machining constraints for ceramic magnets? Ceramic magnets require special machining techniques, and should be machined in an “un-magnetized” state. We are fully equipped to machine these materials to your specifications, just let us know what you are looking for by sending us a special request.
- Are surface treatments required for ceramic magnets? Ceramic magnets do not need to be protected for surface rust. A thin film of magnet powder on the surface is common.
- What are some bonding applications for ceramic magnets? Ceramic magnets are often assembled into products using "superglues" such as Loctite 325 or other epoxies. Please always ensure that bonding surfaces are clean and dry prior to bonding.
- What safety precautions should be taken into consideration when working with ceramic magnets? Ceramic Magnets are hard & brittle, and they can chip or break if dropped or snapped together, so please take special care when handling these magnets!
Bonded Magnets
Bonded magnet materials can be made from Ceramic, NdFeB, or SmCo powders which are combined with a variety of plastic binders (Matrix). They can be either Injection Molded or Compression Bonded into complex magnet shapes with finished dimensions. Bonded magnet materials have a moderate resistance to corrosion and a low tolerance to heat because of the binder material. Bonded magnets are commonly used in automotive parts because they lend themselves to large production quantities and complex shapes can be produced at a low cost.
How to Safely Seperate Your Magnosphere Magnets?

CORRECT
- Slide one magnet off the top of the stack.
- Once off thestack,carefully start lifting the magnet.
- Lift the magnet to free it from the stack.
INCORRECT
- DO NOT attempt to pull, lift, or pry amagnet from the stack before sliding it to the side.
- DO NOT throw away the white storage spacers.
- DO NOT allow the magnets to snap to each other or any magnetic surface. doing so may cause magnets to break!
 NdFeB
NdFeB
Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnets are a type of rare earth alloy with typical atomic structure of Nd2Fe14B which stands for 2 atoms of Neodymium, 14 atoms of Iron(Fe) and one atom of Boron. The sintered Neodymium Iron Boron magnet has higher magnetic properties compare to Samarium Cobalt magnets, however it is more easily oxidized and generally does not have the same temperature resistance. The highest energy products for Neodymium Iron Boron could reach 52 MGOe commercially or more.
Magnosphere is a manufacturer of standard and custom rare earth magnets for the OEM industry. Materials used include sintered and bonded neodymium iron boron, samarium cobalt, aluminum nickel cobalt, ferrite (ceramic), and rubber. Available in various shapes and forms, including discs, rods, plates, cubes, rings, tubes, and spheres. Various magnetization options available. Applications include retail fixtures, motors, sensors, and many more. Magnets for whiteboards, glass boards, and mounts are also available. Capabilities include plating, coating, magnetization, design, simulation, 3D printing or prototyping, plastic injection molding and production. Services include assembly, testing magnetic materials BH curves, coating, plating, engineering design, magnetizing, marking, identification, stabilization, calibration, testing & certification. Markets served include aerospace/defense, medical, industrial, research labs, semi-conductor & telecommunications. JIT delivery!
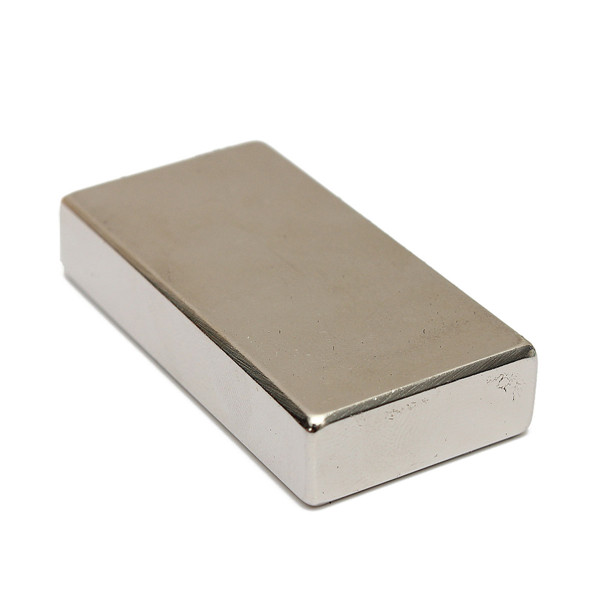
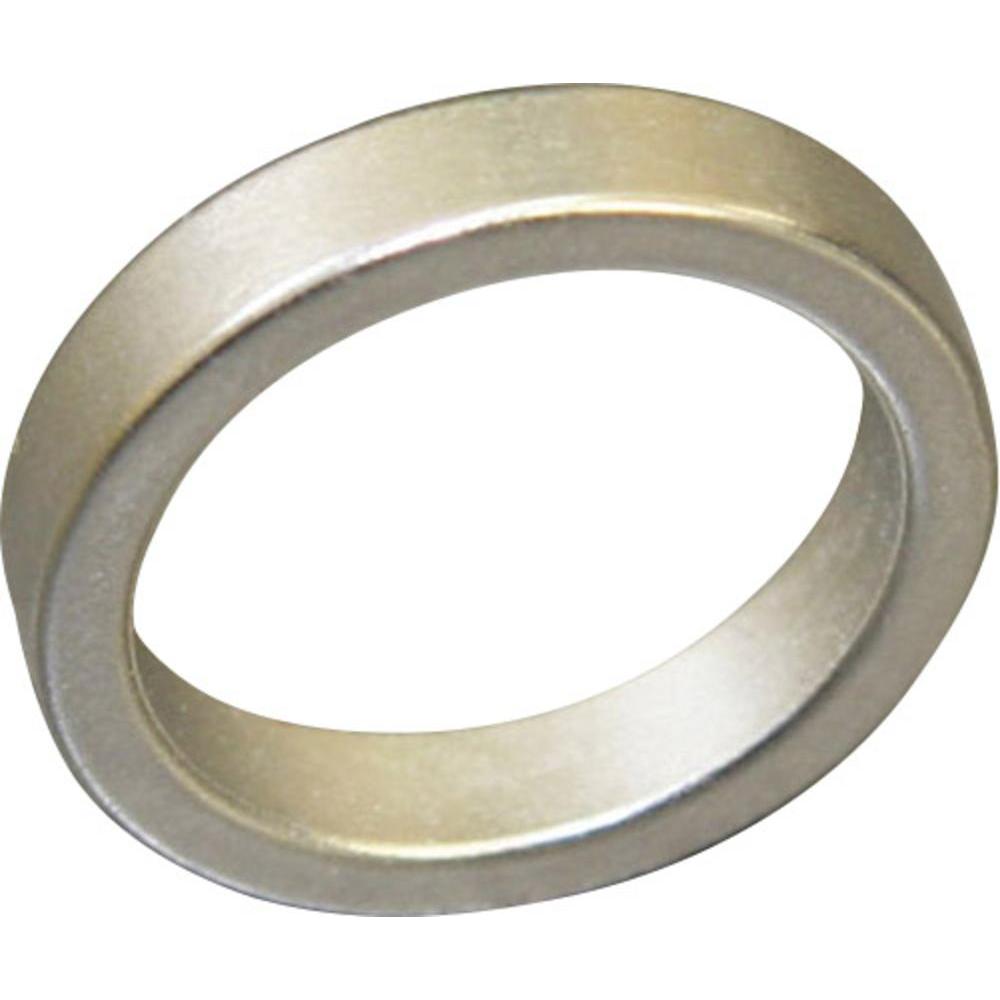
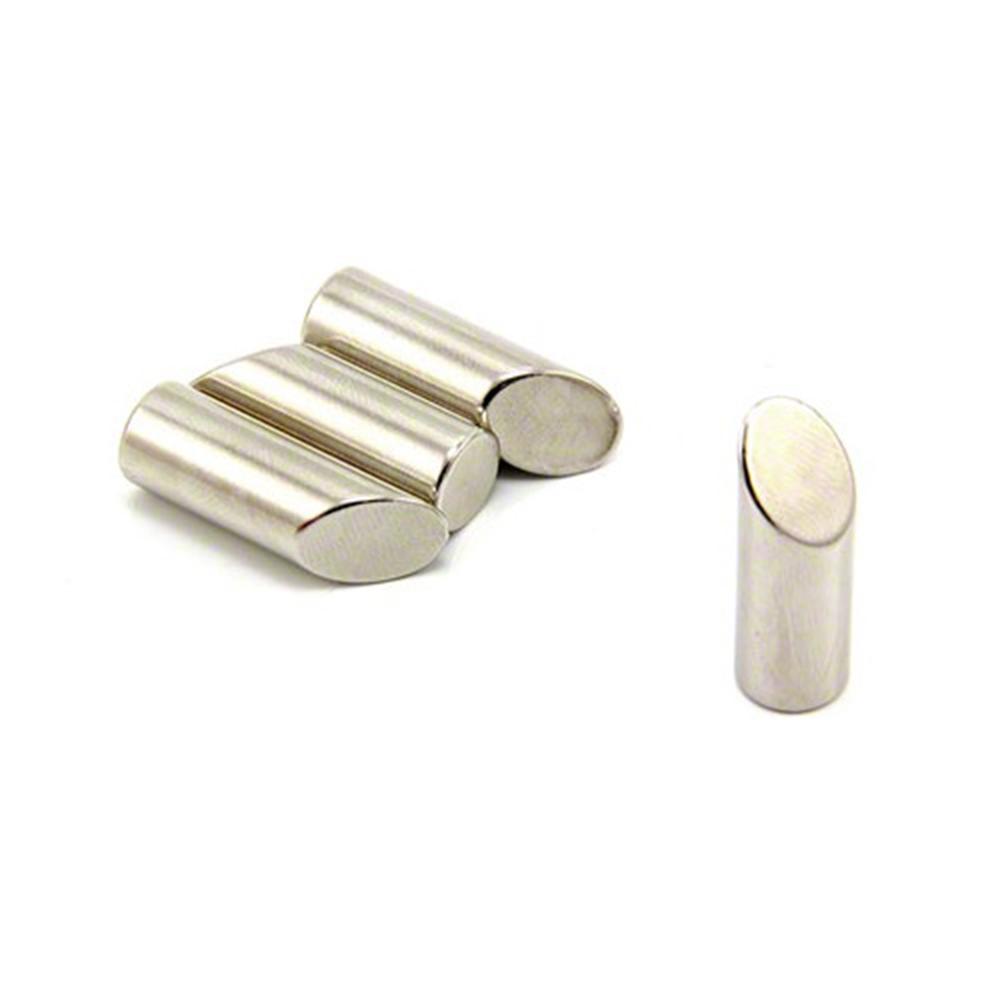
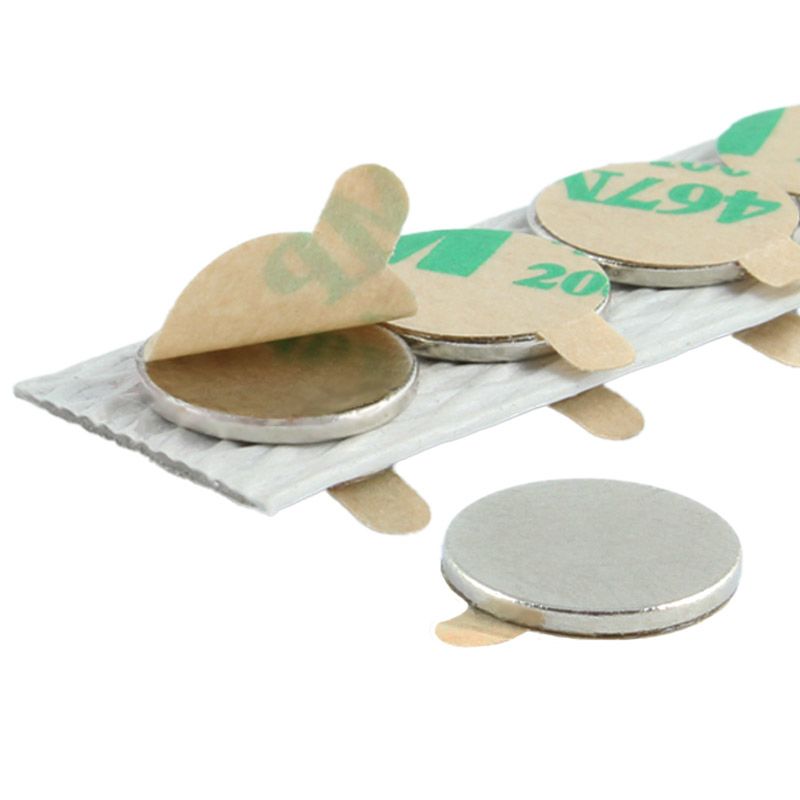
 Neodymium magnets can be fabricated into many shapes and types:
Neodymium magnets can be fabricated into many shapes and types:
 |
When buying magnets, be sure to read our safety instructions before using the magnets to avoid injury. A powerful neodymium magnet is not a toy!
 What are Rare Earth Magnets?
What are Rare Earth Magnets?
Rare earth magnets, also known as neodymium magnets or samarium cobalt magnets are magnets made from alloys of rare earth elements. They are currently the strongest type of permanent magnets made, and produce significantly stronger magnetic fields than other types such as ceramic or alnico magnets. Rare earth magnets have replaced alnico and ferrite magnets in many applications, including head actuators for computer hard disks, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),loudspeakers and headphones, several types of motors, and more.
 Neodymium (Rare Earth) Magnets: the strongest magnets in the world
Neodymium (Rare Earth) Magnets: the strongest magnets in the world
Magnosphere offers best priced Neodymium magnets globally. Please inquire for custom Neodymium magnets or magnetic assembly. Neodymium is the strongest available magnet alloy at up to 52MGOe. The use of Neodymium results in smaller, more cost-effective magnet solutions replacing older materials like Alnico and Ceramic in many applications. Magnosphere.can help optimize performance and cost with Neo magnets in grades from 33 to 52MGOe and operating temperatures up to 230°C/446°F. (NdFeB) Neodymium, a rare earth magnet, is made up of Neodymium Iron and Boron and is moderate in price. A neodymium iron boron magnet is usually plated or coated (Examples: Nickel Plated, Epoxy Coated, Parylene Coated). Neodymium permanent magnets usually offer the best value when comparing price and performance. Stock Neodymium magnets are available in large quantities and dimensions.
 Rare Earth Neodymium NdFeB
Rare Earth Neodymium NdFeB
We provide a range of high magnetic strength Rare Earth Neodymium magnets including Disc magnets, Deep Pot magnets, Shallow Pot Neodymium and Round flat neodymium magnets,
- Neodymium NdFeB magnets are, size for size, the strongest type of any magnet material that is commercially available.
- Neodymium NdFeB magnets are often the ideal first choice for many applications because they offer a maximum performance from the smallest magnet volume.
- Neodymium NdFeB should always be coated to guard against the risk of corrosion – NiCuNi, Zinc, NiCuEpoxy and Gold are popular finishes.
Our Magnet-Shop carries a great variety of these powerful magnets to fit many different applications and they are in stock for immediate delivery!
 Neodymium NdFeB magnets and their application!
Neodymium NdFeB magnets and their application!
At Magnosphere.co.uk, we sell custom Neodymium NdFeB magnets and custom magnetic assemblies so we can help you find the best fit for your project. Some of the common applications of the rare earth magnets are:
- Motors and Generators
- Meters
- Automotive (clamps, sensors)
- Aerospace
- Separation (rods, grids, etc) – 10-12kG (22-26lbs) systems
- High performance magnetic clamps and pot magnets
- They are used in computer hard drives.
- Rare earth magnets also find their utility in high-end speakers.
 Based on the applications and properties earth magnets are of two types:
Based on the applications and properties earth magnets are of two types:
- Neodymium Magnet
- Samarium-Cobalt Magnet
 Process of Making Rare Earth Magnets
Process of Making Rare Earth Magnets
- The rare earth magnets are made by using different process involving various stages. The popular stages of the production of rare earth magnets are:
- The first stage is the manufacture of rare earth element alloys.
- The metal alloy is then finely powdered.
- The next step involved is pressing of powder either isostatically or pressing through die process.
- The particles so pressed are oriented.
- Sintering of the element is done accordingly.
- The shapes are then sliced into desired shapes and sizes.
- The coating is done thereafter.
 Purchase Now: Neodymium Magnets online
Purchase Now: Neodymium Magnets online
|

|

|

|

|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

|

|
We ship our Magnets worldwid via Sea or Air Shipment

Buy Neodymium Rectangular Magnets at Magnosphere and get a better deal!
Magnosphere produces magnets at great prices, produced and delivered on time for all areas of industry, automotive, aerospace, electronics as well as in the design sector, trade fair construction, offices and for the home.
We are an ISO certified shop and carry the Trusted Shops seal. We have successfully completed more than 300,000 orders and offer our ever-growing customer base 24/7 customer service.
All items are available for immediate delivery in large numbers with daily dispatch. Our selection is your win! Thousands of satisfied customers! Buy from a company with the highest quality standards and customer service with flexible and diverse payment options and conditions.
We can also custom manufacture these to fit your exact specifications using our in-house global manufacturing facilities and team of experienced engineers. Need high quantities of magnets at the lowest and fairest price possible? Just let us know what you are looking for and contact our Customer Care Team by sending us a request for quote! We'll work with you to determine the most economical way of providing you with what you need.
Trust in our experience and convince yourself of our service and our products and we look forward to welcoming you to our magnet shop at Magnosphere. You are welcome to contact us by eMail: info(at)magnosphere.co.uk. Available 24/7 x 365 and we are also there for you on public holidays! Or just give us a call.
ROHS-Directive
![]() Magnosphere conforms to the RoHs directive and the Reach and PFOS regulations. Directive 2002/96 / EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, of January 27, 2003, on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
Magnosphere conforms to the RoHs directive and the Reach and PFOS regulations. Directive 2002/96 / EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, of January 27, 2003, on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).

- Hotline:+44 (0)1138683670
- Telefax: +49.2241.9594520
- eMail: info@magnosphere.uk
We are very proud to offer excellent customer service. We know that without our clients, we would not be here. If you have any questions about your order or something else, please call or email us!: info(at)magnosphere.uk
24 / 7 x 365 Including holiday periods! Our customer service team is available to help you!






